Understanding the Steel Castings Refine: A Comprehensive Overview for Beginners
The Metal Casting procedure is a basic technique in making that transforms molten metal into strong forms. Beginners should grasp the numerous approaches entailed, such as sand spreading and die spreading. Understanding the materials, design concepts, and security measures is similarly crucial. Each aspect plays an essential duty in attaining effective end results. As one browses these complexities, the concern of exactly how to optimize each action for enhanced results becomes significantly pertinent.
The Basics of Metal Casting
Metal Casting has actually developed over centuries, its essential principles continue to be indispensable and constant to the production procedure. At its core, Metal Casting entails the makeover of molten steel into solid items via various methods. The procedure begins with the production of a mold, which specifies the form of the final item. Once the mold is prepared, metal is heated up to its melting point and put right into the tooth cavity. After cooling down, the steel strengthens, taking the shape of the mold and mildew.
There are numerous casting methods, including sand spreading, investment casting, and die casting, each with unique benefits and applications. The selection of strategy depends upon variables such as manufacturing quantity, material type, and desired precision. When cast, the end product may undergo extra processes like machining or surface therapy to accomplish the needed finish and specs. Comprehending these essentials is vital for any individual curious about the area of Metal Casting.
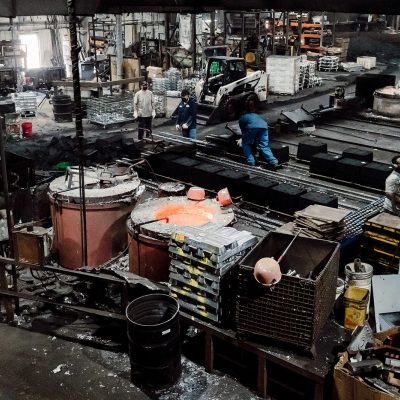

Recognizing Materials Made Use Of in Metal Casting
Materials play a vital role in the Metal Casting process, affecting the last item's homes and efficiency. Different steels are made use of, including aluminum, iron, steel, and bronze, each offering unique qualities fit for specific applications. Aluminum is corrosion-resistant and light-weight, making it optimal for automotive parts. Iron, especially cast iron, is preferred for its superb wear resistance and sturdiness. Steel gives high toughness and adaptability, usually used in heavy machinery components. Bronze, known for its rust resistance and machinability, is commonly employed in marine applications.
Along with the steels, numerous casting materials, such as sand, plaster, and ceramic, are utilized to produce molds. Sand casting, one of the most common method, utilizes silica sand as a result of its thermal security and capacity to develop intricate shapes. Plaster and ceramic molds supply better details but might require more intricate processes. The option of products directly affects the efficiency, cost, and high quality of the spreading procedure.
The Design Process: From Concept to Blueprint
The layout procedure in Metal Casting begins with the initial principle growth, where concepts are created and reviewed. This is adhered to by the application of CAD modeling strategies, enabling accurate visualizations of the style. The plan completion steps assure that all specs are accurately recorded for production.
First Idea Growth
First principle development notes a crucial phase in the Metal Casting process, where concepts change right into substantial layouts. During this stage, developers team up with stakeholders and designers to brainstorm and fine-tune initial concepts. They take into consideration aspects such as functionality, appearances, and manufacturability, making sure that the style fulfills the needed requirements and performance criteria. Illustrations and harsh drafts are produced to visualize the concepts, permitting preliminary analyses of feasibility and cost-effectiveness. This phase additionally includes recognizing products and possible spreading techniques that straighten with the style goals. Eventually, first idea development lays the foundation for an extensive blueprint, leading the subsequent phases of the spreading procedure and ensuring an effective change from concept to reality.
CAD Modeling Techniques
Changing principles into specific layouts, CAD modeling strategies play an essential duty in the Metal Casting procedure. These methods make use of advanced software application to produce in-depth three-dimensional designs that properly mirror the designated product. By using tools such as parametric modeling, strong modeling, and surface area modeling, developers can manipulate measurements and forms with simplicity. CAD systems likewise help with simulation and evaluation, enabling the identification of possible imperfections before manufacturing starts. This proactive strategy minimizes material waste and enhances the design for manufacturability. Furthermore, CAD versions can be conveniently changed, allowing quick iterations based on feedback. Basically, CAD modeling works as the backbone of the design process, connecting the space in between first principles and the ultimate production-ready designs.
Blueprint Completion Steps
Complying with the development of comprehensive CAD models, the following phase includes plan finalization, which is important in translating digital designs into workable strategies for manufacturing. This process begins with evaluating the CAD models for precision and compliance with specifications. As soon as verified, the dimensions, tolerances, and product requirements are carefully described to guarantee clearness. Incorporating notes and notes assists interact important details pertaining to casting processes, surface finishes, and assembly demands. The wrapped up plan undergoes an extensive approval procedure, usually entailing cooperation with designers and production groups to attend to any kind of prospective issues. After all alterations are made and authorizations gotten, the plan is formally launched, serving as the foundational paper for the succeeding stages of Metal Casting, including pattern making and mold and mildew layout.
The Metal Casting Techniques Clarified
Metal Casting strategies include a variety of approaches utilized to shape molten metal into desired forms. These methods vary according to the kind of material, complexity of the layout, and production volume. Sand spreading is among the most usual techniques, involving the production of a mold from sand to hold the liquified metal. Financial investment casting, or lost-wax spreading, permits for complex designs by utilizing a wax pattern that is dissolved. Pass away casting utilizes high-pressure injection of liquified steel into a mold, suitable for automation. Other techniques consist of long-term mold and mildew casting, which uses multiple-use mold and mildews, and centrifugal casting, where rotational forces assist in filling up the mold. Each strategy has its advantages and applications, making it crucial for suppliers to choose the ideal technique based upon their certain requirements and needs. Understanding these strategies is vital for anyone associated with the Metal Casting process.
Ending Up Processes: Enhancing Your Casted Item

Ending up processes play a crucial duty in boosting the quality and look of casted products. Different surface area therapy methods, such as polishing and layer, are used to boost durability and aesthetic appeals. Furthermore, top quality inspection approaches ensure that the final item meets defined criteria and efficiency demands.
Surface Therapy Techniques
A selection of surface therapy strategies play an essential duty in enhancing the high quality and longevity of casted items. These techniques consist of methods such as shot blasting, polishing, and finish. Shot blasting properly removes surface area imperfections, improving the aesthetic and practical features of the spreading. Polishing gives a smooth coating, which is particularly essential for attractive applications and elements needing marginal friction. Coating methods, such as electroplating or powder internet layer, offer added protection against rust and wear, ensuring longevity. Surface treatments can boost attachment for succeeding processes, such as paint or bonding. By using these techniques, manufacturers can accomplish superior surface top quality, which is critical for the efficiency and lifespan of Metal Casting in numerous applications.
Quality Examination Methods
Reliable quality assessment methods are crucial for guaranteeing the stability and efficiency of casted products after the finishing procedures. Various methods are used to evaluate the top quality of Metal Casting, including visual evaluation, dimensional checks, and non-destructive screening (NDT) Aesthetic assessment permits the identification of surface flaws, while dimensional checks ensure that items meet specified tolerances. NDT techniques, such as ultrasonic testing and radiographic assessment, supply much deeper understandings right into interior stability without damaging the spreadings. In addition, mechanical testing, such as tensile and firmness tests, examines product buildings - Aluminum Foundry. By using a combination of these methods, producers can improve product top quality and integrity, ultimately leading to greater customer contentment and lowered production prices
Security Considerations in Metal Casting
While the Metal Casting process uses various advantages, it also presents a variety of security hazards that need to be very carefully managed. Employees in casting facilities are revealed to high temperatures, liquified steels, and harmful products, which can result in extreme injuries if correct preventative measures are not taken. Individual protective tools (PPE) such as heat-resistant gloves, face guards, and protective garments is essential to lessen threats.
Furthermore, the visibility great site of fumes and dust demands proper air flow systems to ensure air high quality - Metal Castings. Normal training on safety and security protocols is important for all staff members to recognize potential dangers and react effectively. Emergency procedures ought to be developed, consisting of fire safety and security actions and emergency treatment schedule. Upkeep of devices and appropriate handling of materials further add to a much safer working setting. By focusing on these safety and security considerations, Metal Casting procedures can shield their labor force and keep effective manufacturing processes
Frequently Asked Concerns
What Are the Environmental Effects of Metal Casting?
Metal Casting can lead to ecological impacts such as air and water air pollution, resource exhaustion, and power intake. Furthermore, improper waste monitoring and exhausts from shops add to eco-friendly disruptions and wellness dangers for close-by areas.
Just how Do I Select the Right Metal for Casting?
To choose the right steel for casting, one should consider factors such as mechanical buildings, corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, and expense. Evaluating the designated application and ecological problems is useful reference important for excellent selection.
What Are the Typical Flaws in Metal Casting?
Common defects in Metal Casting include porosity, contraction, sand incorporation, and misruns. These issues usually arise from incorrect product selection, poor layout, or imperfections in the casting process, influencing the last item's quality and performance.
Exactly How Can I Boost My Steel Casting Skills?
To improve Metal Casting skills, one must exercise consistently, study casting methods, analyze previous projects for problems, look for responses from seasoned casters, and constantly try out various materials and methods to improve proficiency and understanding.
What Is the Expense of Beginning a Metal Spreading Business?
Starting a steel spreading business typically requires an initial investment of $5,000 to $50,000, depending upon devices, products, and facility costs. Elements like place and scale can significantly influence overall startup costs.
The Metal Casting process is a basic technique in producing that transforms molten steel right into solid types. Novices need to comprehend the different approaches entailed, such as sand spreading and pass away casting. There are numerous casting approaches, consisting of sand spreading, financial investment casting, and die casting, each with one-of-a-kind benefits and applications. Investment spreading, or lost-wax casting, enables for complex designs by using a wax pattern that is thawed away. Other methods include permanent mold spreading, which uses recyclable molds, and centrifugal spreading, where rotational pressures assist in filling up the mold and mildew.